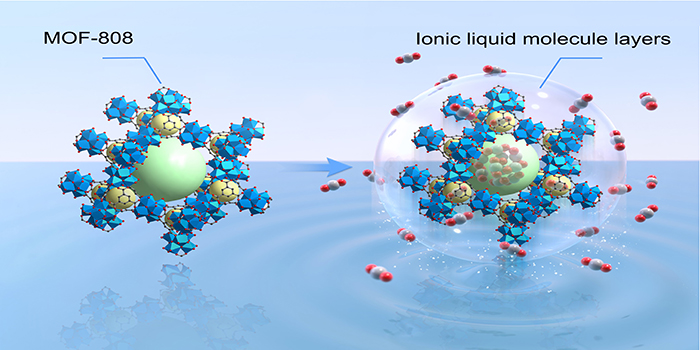
Ionic liquid molecule layers (ILMLs) were assembled on MOF-808 with high porosity for gas adsorption. ILMLs, as a result of better affinity to CO2, perform like an adhesive layer to trap CO2 and MOF-808 performs as a gas reservoir. Deliberately controlling the thickness of ILMLs from 1.7 to 18 nm, we strike a balance of capacity, selectivity and cycling performances for CO2 capture. The optimal composite adsorbs substantial amount of CO2 at ambient conditions (3.00 mmol g−1), which is 2.6 times of that on MOF-808 (1.15 mmol g−1). CO2/N2 selectivity towards mimic combustion flue gas in industry, was 372 (towards 15 mol.% of CO2 in N2) and 478 (towards 5 mol.% of CO2 in N2), near one-order magnitude higher than MOF-808 and exceeding most benchmark materials. Notably, by overcoming the gas–liquid interface limitation, CO2 capacity on each gram of ILMLs was 1000 times higher than that of the bulk liquid. The composite presents cycling separation performances with great energy efficiency for mimic flus gas, as a complete regeneration can be freely achieved at ambient temperature. This work has been published in Chemical Engineering Journal.
The article links:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1385894722011500