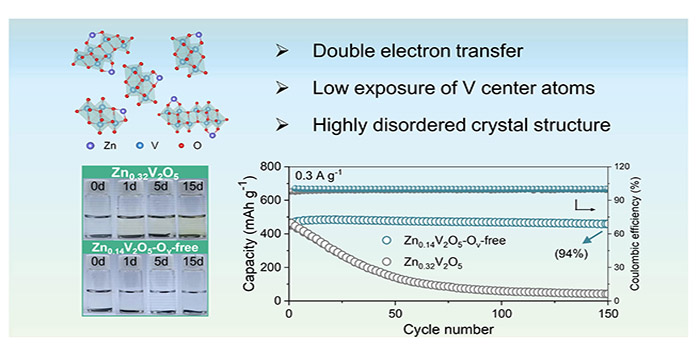
Vanadium-based cathodes have attracted extensive attention in aqueous zinc-ion batteries (AZIBs) because of their high theoretical capacity. However, the development of high-performance vanadium-based cathodes and the establishment of effective design principles remain major challenges, hindering the progress of AZIBs technology. In this study, the critical role of structural building blocks ([VO4] tetrahedra, [VO5] square pyramids, and [VO6] octahedra) is unveiled in vanadium-based oxides, demonstrating their distinct contributions to both capacity and stability. Among these, [VO6] octahedra stand out for their superior capacity and stability, making vanadium oxides with [VO6] octahedra promising candidates for AZIBs cathodes. Furthermore, it is shown that the presence of oxygen vacancies undermines the stability of [VO6] building blocks by increasing the exposure of the vanadium sites. Based on these findings, amorphous vanadium oxide (ZVO-Ov-free), composed of oxygen vacancy-free [VO6] octahedra arranged in short-range-ordered chains, is synthesized, maximizing the utilization of highly active vanadium sites. The ZVO-Ov-free cathode achieves a specific capacity of up to 483 mAh g−1 at 0.3 Ag−1, with a capacity retention of 94% after 150 cycles. These findings provide valuable insights for the rational design of vanadium-based oxides at the atomic and framework levels, paving the way for the practical development of AZIBs.
The article links: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/smll.202502723