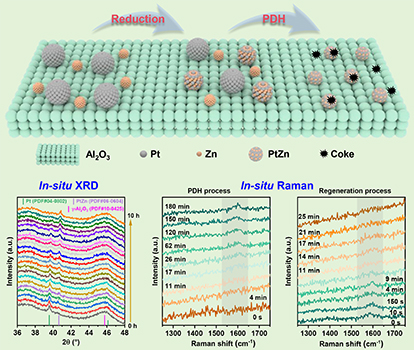
Our group developed a series of PtZn bimetallic catalysts via a combined co-impregnation and temperature-programmed reduction strategy. Through complementary ex-situ and in-situ characterization techniques, we elucidated the dynamic evolution of active sites and coke deposition behavior. During either reduction pretreatment or propane dehydrogenation (PDH) reactions, the initially large Pt nanoparticles transformed into highly dispersed PtZn alloy clusters, typically considered as the active sites for dehydrogenation. These PtZn alloy clusters demonstrated exceptional intrinsic capability for C-H bond activation while effectively suppressing C-C bond cleavage Furthermore, in situ Raman spectroscopy was employed to monitor the dynamic evolution of coke during dehydrogenation and regeneration cycles. The study revealed that the catalyst's dehydrogenation activity and stability correlated with coke formation rates, while coke removal efficiency depended critically on its deposition location. By establishing the structure-activity relationship between the evolution of active sites and coke formation/removal processes, this study provides critical theoretical insights for the rational design of high-efficiency Pt-based dehydrogenation catalysts. This work has been published in Chemical Engineering Journal.
The article links:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2025.165040